At the recent Qualcomm Snapdragon 820 Southeast Asia showcase, we were given a deep-dive into some of the most interesting features Qualcomm has incorporated into the Snapdragon 820. Here’s a taste of what these new technologies are, and how they help make the smartphone experience that much better.
1. New Custom-Designed Kryo CPU
One main reason why Qualcomm’s 2015 chips were disappointing was the fact that Qualcomm used ARM-based Cortex cores. This was different from the 2014 range of Snapdragon processors, where they used Qualcomm-designed “Krait” custom CPUs.
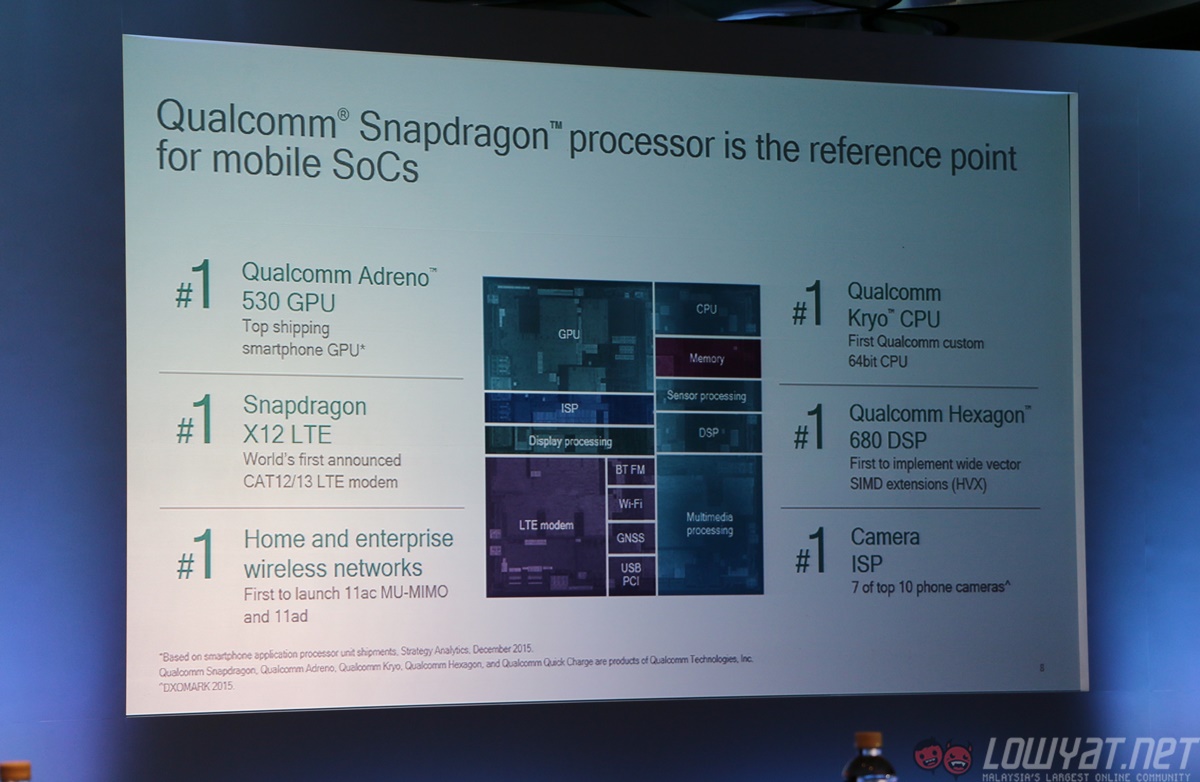
This year, Qualcomm finally unleashed its Kryo CPU design, which is Qualcomm’s first custom 64-bit quad-core CPU, manufactured using the advanced 14nm FinFET process. It maximises performance while retaining Qualcomm’s exemplary power efficiency; despite being a quad-core chip, it easily trumped the Snapdragon 810 in various benchmarking tools – it also does not suffer from thermal throttling issues.
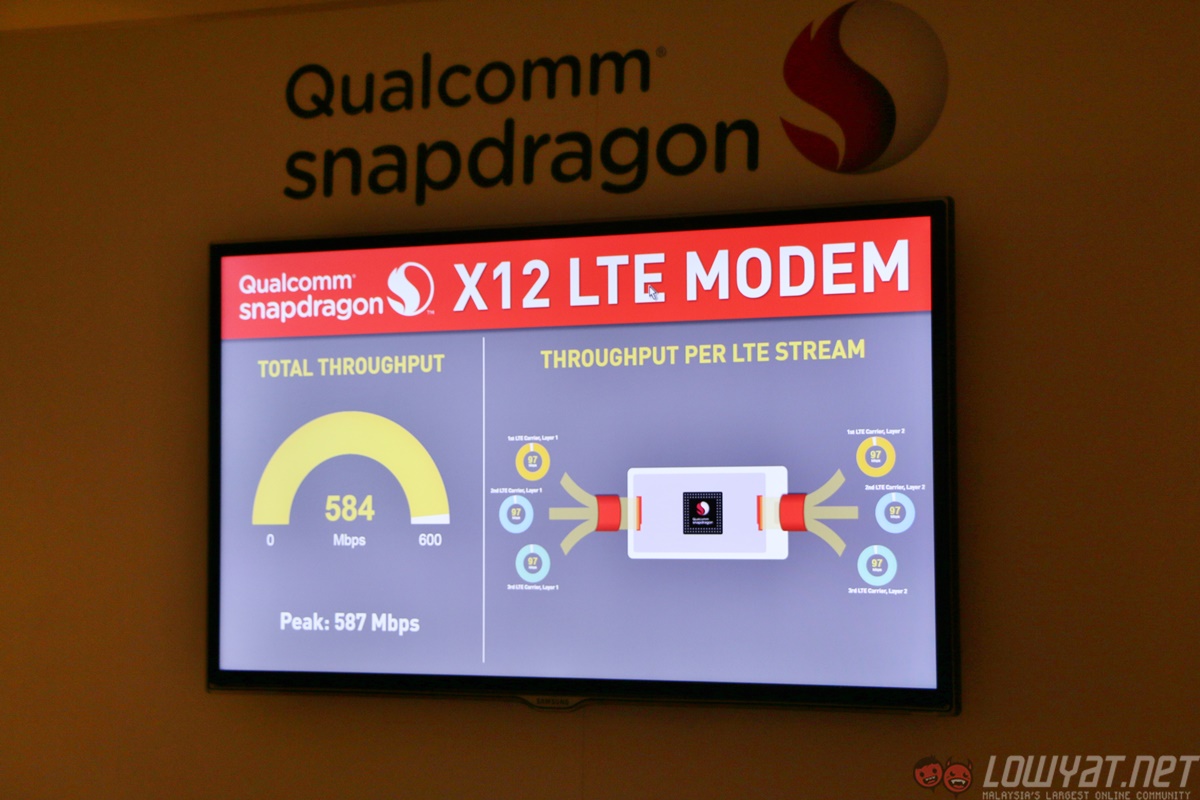
2. X12 LTE Modem
In its early days, Qualcomm dabbled mainly in the mobile modem business, before quickly moving into the chipset business it dominates today. This legacy is clearly visible in the modems found in today’s Snapdragon SoCs. The Snapdragon 820 features the X12 LTE modem, offering LTE download speeds of up to 600Mbps and upload speeds of up to 150Mbps, up 33% and 200% respectively from the modem found on the Snapdragon 810.
It is also one of the few mobile modems to feature support for Multi-User MIMO, 11ad multi-gigabit WiFi, and what many consider to be the next big thing in LTE: LTE-U.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0t311N68o9w
As if that isn’t enough, Qualcomm already has the X16 LTE modem lined up and ready to launch in the second half of this year. When it is launched, it will be the first mobile modem to support download speeds of up to 1Gbps, as well as support for LTE-U.
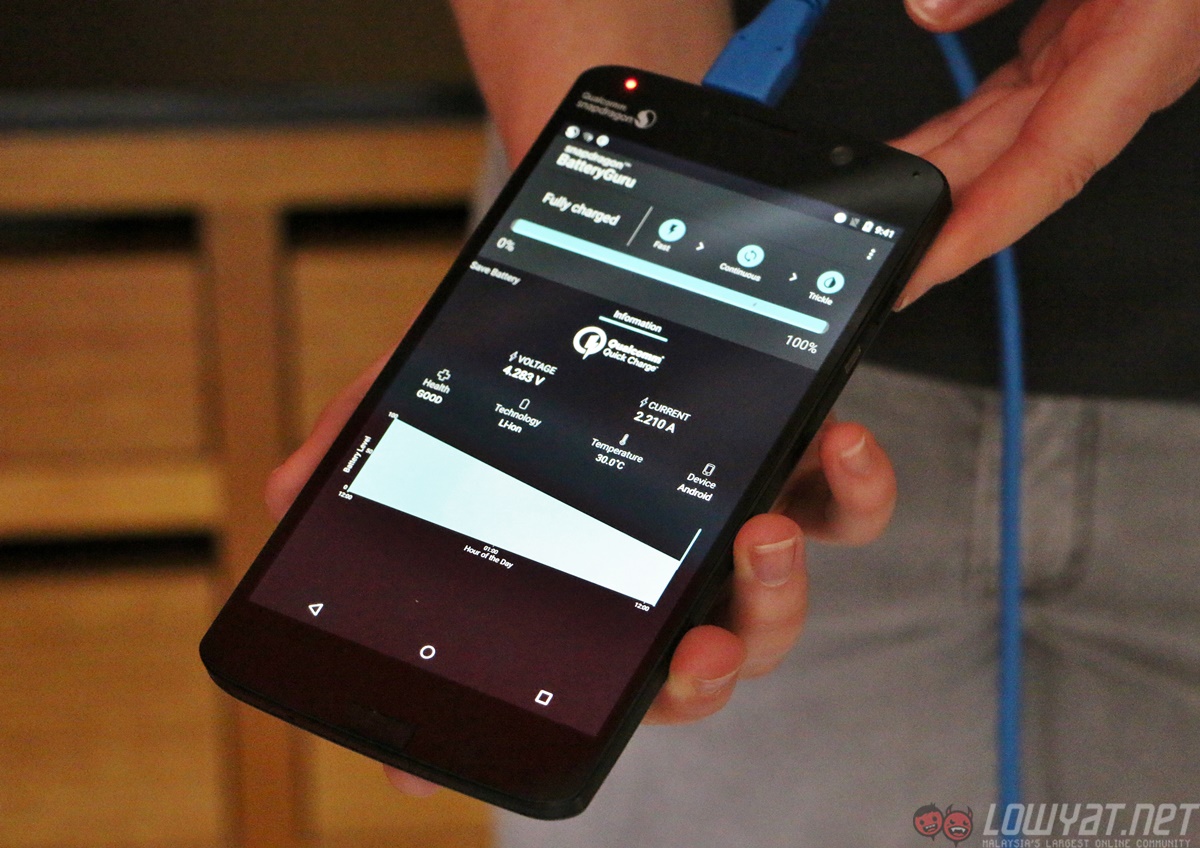
3. Quick Charge 3.0
Perhaps the most familiar feature for most smartphone users, Quick Charge 3.0 builds upon Quick Charge 2.0’s success, featuring even faster charging times over short periods of time.
This is in tune with today’s consumer trend where users “snack” on charging, especially those who are always on the move. Whether it is a quick break at your desk before the next meeting, or even during the meeting itself, fast charging capabilities have become essential for the smartphone user.

Quick Charge 3.0 is up to two times faster than Quick Charge 1.0, and is capable of charging a 2,750mAh smartphone battery from zero to 80% in about 35 minutes. It is also up to 38% more efficient than Quick Charge 2.0, with a new feature called Intelligent Negotiation for Optimum Voltage (a complicated name for an equally complicated process which automatically selects ideal voltage for each smartphone).
4. Snapdragon Sense ID
Most smartphones today use a capacitive-based fingerprint scanner. It uses tiny electrical charges which are capable of mapping out the microscopic ridges and valleys that make up a fingerprint, and store them for comparison later on (i.e. when you unlock your phone with your fingerprint). It is highly secure, and just as accurate.
However, since capacitive scanners require some form of electrical discharge when the finger is placed on the scanner, they need to be situated as close to the finger as possible. Qualcomm’s new Sense ID technology, supported on the Snapdragon 820 chip, negates that need.
Sense ID is vastly different from any fingerprint scanner found today. It uses ultrasonic sound waves to penetrate the skin and capture a 3D map of the fingerprint. It is able to capture more information that a capacitive sensor cannot, such as ridge endings and even sweat pores. Because it captures a 3D map of the fingerprint, Sense ID is touted as the most secure fingerprint scanning solution today.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0df9m0qTo-8
On top of that, there are two additional benefits of Sense ID’s ultrasonic mapping technology. First, Sense ID can successfully recognise a fingerprint even through contaminants such as oils, sweat, and lotions.
Finally, since ultrasonics penetrate through thicker materials, Sense ID scanners do not need to be placed as close to the device’s surface. This opens up more design options, and lets smartphone makers try out new ways of implementing Sense ID scanners.
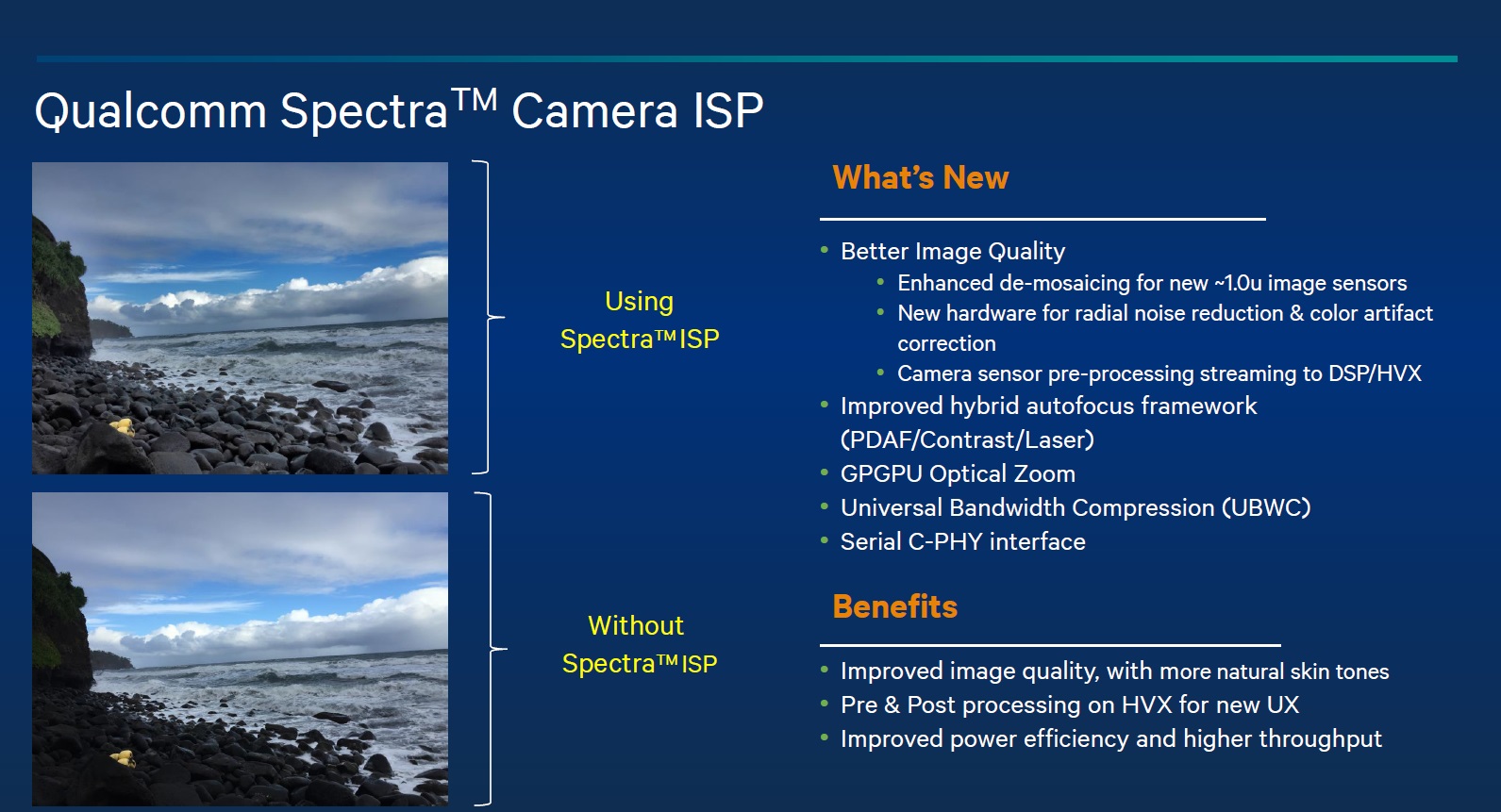
5. Qualcomm Spectra ISP
 (Image: Image Sensors World)
(Image: Image Sensors World)
Companies like Samsung, Apple and LG spend a significant amount of R&D resources into refining the smartphone camera experience, creating independent image signal processors (ISPs) that handle the smartphone camera’s post-processing.
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 820 chip features its own ISP, which aids smartphone makers that do not have the resources to develop its own. Called Spectra, it is a 14-bit dual image signal processor that supports up to 25MP camera sensors, and feature a “flexible hybrid” framework made up of phase detection, contrast and laser-guided autofocus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=etggvMP-nzM
The Spectra ISP is also designed to offer up to 25% longer battery life when recording in HD or 4K videos. There’s also Snapdragon LLV (Low Light Videos), which adaptively brightens parts of the frame that are too dark in photos and videos. Besides that, the Spectra ISP also sports something called Touch To Track, an algorithm-based feature that recognises and locks onto desired objects and then adaptively zooms and tracks them in video recording.
Perhaps most excitingly, the Spectra ISP supports up to three camera sensors – one facing the user, and two facing the rear. Dual-sensor setups allow the Spectra ISP to capture depth and enable 3D reconstruction; this data is what lets users “refocus” images after they have been captured.
————–
It is safe to say 2015 wasn’t the best of years for chipmaker Qualcomm. Its range of Snapdragon system-on-a-chip (SoC), especially the flagship-class Snapdragon 810 and popular mid-range Snapdragon 615 processors all had well-known issues ranging from overheating, high battery usage, and disappointing performance.

So why is it that this year’s flagship smartphones, including LG G5, Xiaomi Mi 5, Samsung Galaxy S7, and plenty others, are all powered by the Snapdragon 820? Qualcomm’s flagship SoC for 2016 is quickly erasing the memories of 2015, with all-new features that ensure Qualcomm’s position as the premier smartphone chipmaker remains unrivalled.
Follow us on Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or Telegram for more updates and breaking news.